LAN Switching Configuration
LAN switching enables users to resolve bandwidth issues by increasing the efficiency of LANs using VLAN and port trunking technologies.
Configuring VLAN Settings
A virtual LAN (VLAN) groups multiple network devices together and limits the broadcast domain. Members of a VLAN are isolated and network traffic is only sent between the group members. You can use VLANs to increase security and flexibility while also decreasing network latency and load.
When using both port trunking and a VLAN, port trunking must be configured first.
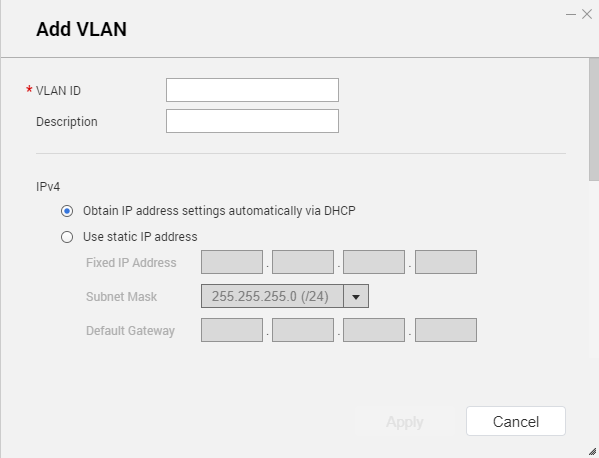
Network & Virtual Switch adds the VLAN.
Configuring Port Trunking Settings
Port trunking combines two or more Ethernet interfaces for increased bandwidth, load balancing and fault tolerance (failover). Load balancing is a feature that distributes workloads evenly across multiple Ethernet interfaces for higher redundancy. Failover ensures that a network connection remains available even if a port fails.
Before configuring port trunking settings, ensure at least two network interfaces are connected to the same switch.
Network & Virtual Switch applies the pork trunking settings.